Sigma is a set of standards and techniques used to improve the quality of products and services. It is a data-driven approach to problem solving that uses statistical analysis, process improvement, and experimental design. Six Sigma focuses on reducing variation in processes, eliminate defects, and improve customer satisfaction. It is used by many organizations to increase efficiency and reduce costs.
Six Sigma Quality Improvement and Management (QIM) is a quality management approach that applies Six Sigma principles to improve processes and increase customer satisfaction. QIM focuses on identifying areas where process improvements can be made, and measure performance against set standards, and analyze the root causes of problems, and implement solutions, and monitor results over time, and constantly improving operations. By applying these principles in all areas of the organization’s operations, QIM can help companies be more successful in achieving their quality improvement goals.
Six Sigma Concept
Six Sigma is an objective and controlled strategy and action plan. In her work, she relies on collecting and analyzing data in order to eliminate defects. The main objective of this methodology is to know the defects and identify them accurately, which enables them to be solved and avoided. Hence, good brand management and maximum customer satisfaction.
From a technical point of view, We can say that Six Sigma is a level of operation at which the error probability does not exceed 3.4 errors per million. and the error here, It is every deviation in the product, service, or production and sales process from the customer’s requirements. In a more precise sense, everything that would raise the customer’s dissatisfaction with what was provided to him.
The Greek letter “sigma σ” is a statistical term. It measures how far a particular process has deviated from perfection. Sigma is also known as the process standard deviation from the mean. The Six Sigma process allows an organization to measure the number of “defects” in the process. And ways to eliminate them and get as close to “zero defects” as possible.
History of Six Sigma
The roots of the principles of quality enhancement and product improvement go back to the beginning of the twentieth century. Many ideas and efforts aimed at improving the quality of products began to appear in order to reduce waste rates. The first initiatives aimed at improving quality were those undertaken by Motorola to increase the quality of its products and reduce production costs, This is in an effort to reduce the percentage of defects contained in the products to almost zero within five years.
This marked the beginning of the actual application of Six Sigma as an important methodology for quality improvement. after that, Six Sigma has been adopted as a methodology for solving and developing businesses. Thanks to the results achieved, the use of Six Sigma standards has evolved to include other fields besides the manufacturing sector, education, and health care.
Six Sigma relationship to quality
The emergence of defects in products constitutes a real threat to the reputation of companies, costing them millions of dollars in losses. In addition to damaging their trademarks. And we recall here, An example is the battery explosion of Samsung phones, which prompted it to withdraw about a million Galaxy Note 7 phones after a succession of battery explosions of this model. Which made the path to corporate success fraught with danger.
From this point, The importance of quality management appears through the Six Sigma strategy because it simply imposes many strict standards that must be respected at every stage of the production chain. Taking care to abandon useless processes that can be left without negative impact. Respecting and applying this approach rigorously and objectively will ensure the best results for companies and customers alike. This enhances quality levels and thus increases brand loyalty.
Benefits of applying Six Sigma
1. Improving customer loyalty
All organizations seek to maintain the loyalty of their customers. Of Course, This Can Only Be Achieved Through High Levels Of Quality, The Absence Of Which Is The First Reason For Losing Customer Loyalty. Here, the importance of Six Sigma is evident, as its application reduces the risk of obtaining dissatisfied customers. It helps in conducting customer studies that contribute to identifying the essential attributes for their satisfaction.
2. Time management
The use of the Six Sigma methodology will have positive effects on managing time and controlling task management effectively, It increases the performance and productivity of employees. It becomes possible to use the time more wisely. On the other hand, Six Sigma teams within companies can reduce the work cycle time by identifying problems and obstacles that will extend the work cycle life.
3. Motivating employees
The development of employees’ performance is associated with the availability of incentive factors that would encourage them to give in a better way. Indeed, the problem-solving tools provided by Six Sigma allow for the development of employees and create the conditions and systems that motivate employees to carry out the tasks assigned to them.
4. Ensure compliance, reduce risks and eliminate defects
Six Sigma requires high quality standards. for this reason, A large number of vendors, suppliers and regulatory institutions apply Six Sigma standards when evaluating products or accounts. This requires various companies to comply with international standards of quality. Six Sigma standards are characterized by reducing the percentage of waste that results from the high percentage of defects.
5. Higher returns and lower costs
Increasing the amount of profits is crucial, Six Sigma allows business owners to take a deeper look at their operations. make wise decisions based on facts, They usually lead to improved quality and maximization of profits. The higher the quality of your products and services, Your earnings have increased.
Six Sigma implementation stages
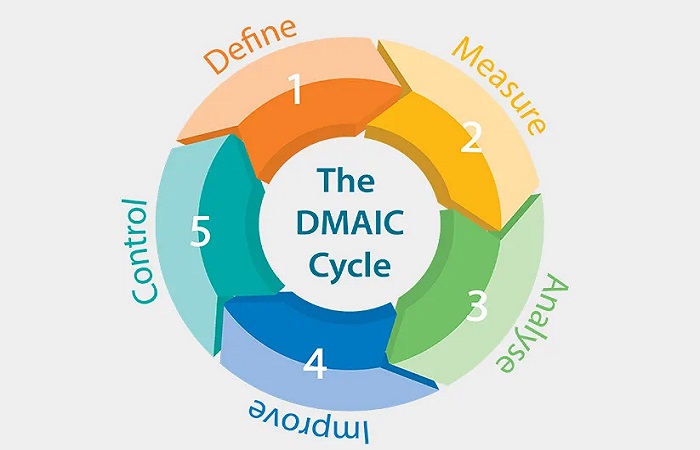
The sigma level can be calculated by counting the number of errors and defects in the products or services provided to the customer. This level is determined on the basis of the number of defects or errors that occur in each million products or services. The implementation of Six Sigma requires respecting its clear methodology based on the following five steps:
Definition: What problem do you want to solve? The definition stage is the first stage of the improvement process. At this stage, the project team works to identify and identify the problems and defects that were encountered.
Measurement: During this phase the focus is on collecting data relevant to the scope of the project. The data collection plan includes what data will be collected and who will collect it and when. After collecting the data, the stage of analyzing it comes to ensure its nature.
Analysis: The focus during the measurement phase is on identifying the main and root cause behind the observed errors and defects. After considering all possible possibilities, We move on to scrutinizing the hypotheses and verifying their credibility. All this in order to reach knowledge and determine the main reason or reasons behind the occurrence of defects affecting the completion of the work.
Development: This phase improves the process by identifying potential solutions, ways to implement them, testing them, and implementing them for improvement. This is within the framework of seeking to reduce the size of risks and respond to the aspirations of customers to enhance the level of satisfaction on their part. After setting up the optimization program, the download process will start immediately. Where procedures are performed that are chosen with the intent of testing their effectiveness.
Control: During this stage, Post-implementation results are evaluated to check progress. With changes, if any. The main objective of this stage is to monitor the solutions to ensure that the required performance is maintained. By validating and developing procedures, In addition to checking benefits and earnings growth. Subsequently, The pivotal goal of the control phase is to ensure that gains can be retained.
A practical example of Six Sigma
A company operating in the field of manufacturing household electronic and electrical appliances. However, it recorded a significant decrease in the volume of sales of its televisions without a clear explanation for this decline. Then the company decided to apply Six Sigma standards, which were as follows:
The first step: The assigned research team attempts to define the problem and then work to develop possible possibilities for the occurrence of the problem of decline in sales without clear reasons. Research has identified the following possibilities: poor quality, marketing fails effectively, hidden damage a negative attitude on the part of customers, Having strong competition.
The second step: measuring these possibilities by researching each possibility to ensure its existence and determine the size of its impact.
The third step: start analyzing the results reached after the completion of the previous steps, which allows in the end to determine the real reason or reasons responsible for the occurrence of this defect (declining sales).
The fourth step: initiating the improvement process after developing the appropriate program for that, which will solve the problem that the company faced regarding the decline in sales of televisions
Step Five: Monitoring the download of the optimization program and tracking its effectiveness and ability to overcome the problem in question, In addition to seeking to maintain the positive results achieved and trying to avoid the recurrence of such a defect in the future.